Detecting mimikatz
Mimikatz is well known and commonly used to dump credentials from memory along with other Windows post-exploitation activity. Mimikatz is mainly known for dumping LSASS. We can hunt for the file created, execution of the file from an elevated process, creation of a remote thread, and processes that Mimikatz creates. Anti-Virus will typically pick up Mimikatz as the signature is very well known, but it is still possible for threat actors to obfuscate or use droppers to get the file onto the device.
Mimikatz file creation config
The first method of hunting for mimikatz is just looking for files created with its name. This is a simple
technique and can allow you to find anything that might have bypassed AV. Most of the time when dealing with an
advanced threat more advanced hunting techniques like searching for LSASS behaviour are needed.
<RuleGroup name="" groupRelation="or">
<FileCreate onmatch="include">
<TargetFileName condition="contains">mimikatz</TargetFileName>
</FileCreate>
</RuleGroup>
Abnormal LSASS behaviour config
We can use the ProcessAccess event ID to hunt for abnormal LSASS behavior. This would show potential LSASS abuse
which usually connects back to mimikatz or some other kind of credential dumping tool.
If LSASS is accessed by a process other than svchost.exe it should be considered suspicious behaviour and should
be investigated further. To aid in looking for suspicious events, use a filter to only look for processes besides
svchost.exe. Sysmon will provide further details to help lead the investigation such as the file path the process
originated from.
To aid in detections, use a custom configuration file:
<RuleGroup name="" groupRelation="or">
<ProcessAccess onmatch="include">
<TargetImage condition="image">lsass.exe</TargetImage>
</ProcessAccess>
</RuleGroup>
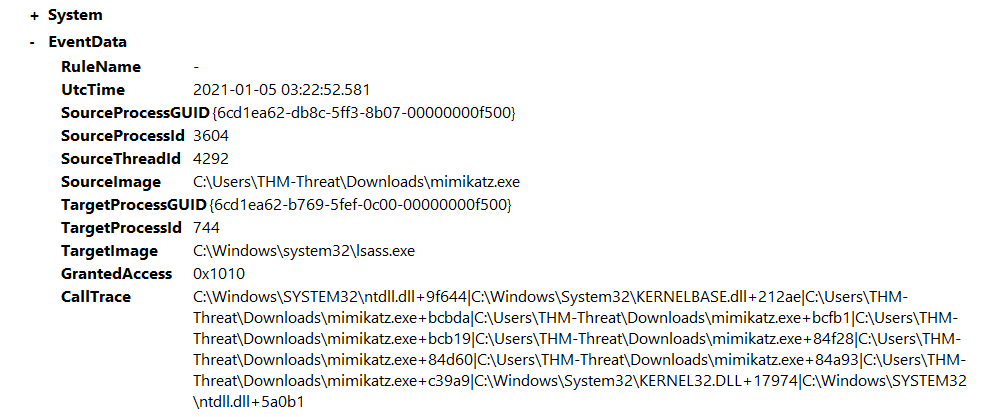
Obfuscated version of mimikatz dumping credentials
Open C:\Users\THM-Analyst\Desktop\Scenarios\Practice\Hunting_LSASS.evtx in Event Viewer to view an attack using
an obfuscated version of mimikatz to dump credentials from memory.
 |
|---|
The event shows the mimikatz process accessed, and there are also a lot of svchost.exe events. |
Alter the config to exclude events with the SourceImage event coming from svhost.exe:
<RuleGroup name="" groupRelation="or">
<ProcessAccess onmatch="exclude">
<SourceImage condition="image">svchost.exe</SourceImage>
</ProcessAccess>
<ProcessAccess onmatch="include">
<TargetImage condition="image">lsass.exe</TargetImage>
</ProcessAccess>
</RuleGroup>
Detecting LSASS Behavior with PowerShell
Use the same XPath queries used in the rule to filter out the other processes from TargetImage.
Get-WinEvent -Path <Path to Log> -FilterXPath '*/System/EventID=10 and */EventData/Data[@Name="TargetImage"] and */EventData/Data="C:\Windows\system32\lsass.exe"'